Table of Contents
1. Understanding Scabies - What is Scabies? - Causes of Scabies - Symptoms of Scabies 2. Diagnosis of Scabies - Medical Examination - Home Diagnostic Methods 3. Conventional Treatments for Scabies - Prescription Medications - Over-the-Counter Treatments 4. Natural Remedies for Scabies - Essential Oils - Herbal Treatments - Homeopathic Solutions 5. Lifestyle Changes to Aid Scabies Treatment - Dietary Adjustments - Skincare Routines 6. Hygiene Practices to Prevent Scabies Spread - Cleaning and Disinfection - Personal Hygiene 7. The Role of Immunity in Scabies Treatment - Boosting the Immune System - Stress Management 8. Scabies in Children and Infants - Special Considerations - Safe Treatment Options 9. Dealing with Scabies in Pets - Identifying Scabies in Animals - Treatment and Prevention 10. Myths and Misconceptions about Scabies - Common Misbeliefs - Scientific Clarifications 11. Emotional and Psychological Impact of Scabies - Coping Strategies - Support Systems 12. Frequently Asked Questions - How long does it take to cure scabies? - Can scabies go away on its own? - Is scabies contagious? - What are the complications of untreated scabies? - How can I prevent scabies reinfestation? - Are there any side effects to scabies treatments? 13. External Resources and Links 14. ConclusionUnderstanding Scabies
What is Scabies?
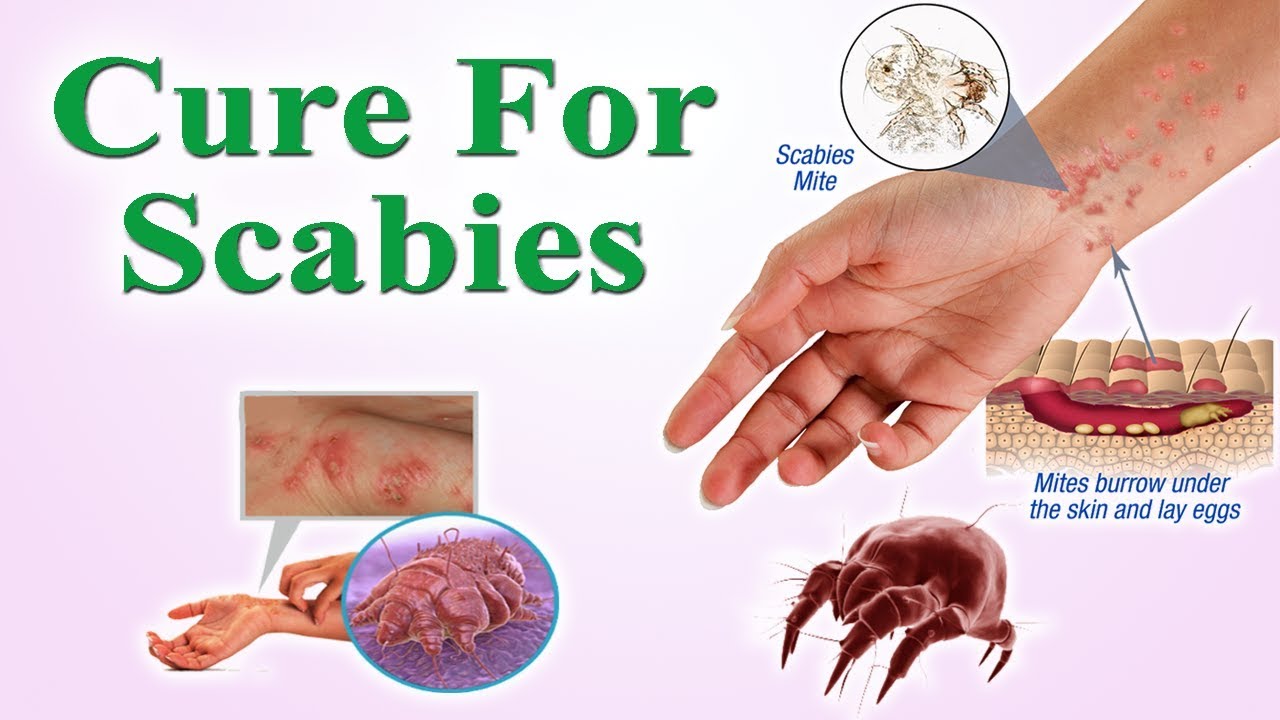
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, a microscopic parasite that burrows into the human skin. This infestation leads to a variety of symptoms, most notably severe itching and a rash. Scabies is transmitted through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infested person, making it common in crowded living conditions and among family members.
Causes of Scabies
The main cause of scabies is the infestation of mites. These mites are tiny, nearly invisible to the naked eye, and they thrive in warm environments. Scabies can spread quickly in places where there is close physical contact, such as households, schools, and care facilities. Factors that increase the risk of contracting scabies include poor personal hygiene, crowded living conditions, and weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of Scabies
The hallmark symptom of scabies is intense itching, which often worsens at night. This itching is due to the body's allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs, and their waste. Other symptoms include a rash that appears as tiny blisters or scales, noticeable in the webbing between fingers, wrists, elbows, and other areas. In severe cases, the skin may develop crusts and sores due to excessive scratching.
Diagnosis of Scabies
Medical Examination
A proper diagnosis of scabies typically requires a visit to a healthcare professional. They may perform a skin scraping to examine under a microscope, confirming the presence of mites, eggs, or mite feces. This process helps rule out other skin conditions with similar symptoms, such as dermatitis or psoriasis.
Home Diagnostic Methods
While a professional diagnosis is the most reliable, there are home methods that can suggest scabies. Observing the typical rash pattern and experiencing the characteristic itching, especially at night, can be indicative. However, these methods are not definitive, and any suspicion should be followed up with a medical consultation for confirmation.
Conventional Treatments for Scabies
Prescription Medications
Once diagnosed, scabies is often treated with prescription medications. These include topical creams and lotions, such as permethrin and ivermectin, which are applied directly to the skin to kill the mites. These treatments are usually effective, but a second round might be necessary if symptoms persist.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
There are also over-the-counter treatments available for scabies, although they tend to be less effective than prescription options. These include creams that relieve itching and inflammation but may not eradicate the mites. Consulting with a healthcare provider before using these treatments ensures they are appropriate for the condition's severity.
Natural Remedies for Scabies
Essential Oils
Essential oils, such as tea tree oil and neem oil, have been found to have anti-parasitic properties, making them effective natural treatments for scabies. These oils help in soothing the skin, reducing inflammation, and eliminating mites. They can be applied directly to the affected areas, but should always be diluted with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation.
Herbal Treatments
Herbal remedies, such as aloe vera and turmeric, offer soothing relief and possess anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Aloe vera gel can be applied to the skin to alleviate itching, while turmeric paste can reduce swelling and kill mites. These treatments are popular for their natural healing properties and minimal side effects.
Homeopathic Solutions
Homeopathy offers alternative remedies for scabies, focusing on strengthening the body's natural defenses. Remedies such as sulphur and graphites are commonly used, and while scientific support is limited, many individuals have reported relief from symptoms. Consulting a qualified homeopath is recommended to determine the best remedy for individual cases.
Lifestyle Changes to Aid Scabies Treatment
Dietary Adjustments
A healthy diet can aid in the treatment of scabies by supporting the immune system. Consuming foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as zinc, can enhance skin health and reduce inflammation. Avoiding sugar and processed foods may also be beneficial, as these can exacerbate symptoms and slow down recovery.
Skincare Routines
Implementing a gentle skincare routine is essential when treating scabies. Avoiding harsh soaps and using moisturizing creams can prevent skin irritation and promote healing. Regularly washing bedding and clothing in hot water helps remove mites and prevent reinfestation. Maintaining overall skin health is crucial for a speedy recovery.
Hygiene Practices to Prevent Scabies Spread
Cleaning and Disinfection
Maintaining cleanliness in the home is vital to prevent the spread of scabies. Regularly vacuuming carpets and upholstery, washing clothes and linens in hot water, and disinfecting surfaces can help eliminate mites. It is also important to isolate personal items such as towels and bedding to prevent cross-contamination.
Personal Hygiene
Practicing good personal hygiene is crucial in managing scabies. Regular bathing and handwashing can reduce the risk of spreading the mites. Sharing personal items such as towels, clothes, and bedding should be avoided, as these can easily transmit scabies between individuals.
The Role of Immunity in Scabies Treatment
Boosting the Immune System
A strong immune system can help the body fight off infections, including scabies. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports immune health. Regular exercise and adequate sleep are also important factors in boosting immunity and accelerating recovery.
Stress Management
Stress can weaken the immune system, making it more challenging to combat infections. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can positively impact immune function. Maintaining a positive outlook and seeking support from friends and family can also aid in managing stress during scabies treatment.
Scabies in Children and Infants
Special Considerations
Scabies in children and infants requires special attention due to their sensitive skin and developing immune systems. Symptoms in children may present differently, such as irritability and difficulty sleeping. It is crucial to consult a pediatrician for an appropriate treatment plan that is safe and effective for young children.
Safe Treatment Options
For infants and young children, treatment should be gentle and non-irritating. Mild topical creams prescribed by a healthcare provider are often recommended, and natural treatments such as diluted essential oils may also be considered. Close monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare professional ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Dealing with Scabies in Pets
Identifying Scabies in Animals
Pets can also be affected by scabies, known as mange in animals. Symptoms include excessive scratching, hair loss, and skin irritation. It is important to take pets to a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan to prevent the spread of scabies to humans and other animals.
Treatment and Prevention
Veterinary treatment for scabies in pets typically involves topical or oral medications that eliminate mites. Regular grooming and maintaining a clean environment can help prevent future infestations. Pet owners must also ensure that their living areas are free from mites to protect both pets and humans.
Myths and Misconceptions about Scabies
Common Misbeliefs
There are several myths surrounding scabies that can lead to misunderstandings and ineffective treatments. One common misconception is that scabies is caused by poor hygiene, when in reality, it is primarily spread through close contact. Another myth is that scabies can only affect certain demographics, but it can infect anyone regardless of age or cleanliness.
Scientific Clarifications
Understanding the facts about scabies can help dispel myths and encourage effective treatment. Scabies is a medical condition caused by mites, not a reflection of personal hygiene or socio-economic status. Scientific evidence supports various treatment options, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Scabies
Coping Strategies
Dealing with scabies can have a significant emotional and psychological impact due to the discomfort and social stigma associated with the condition. Coping strategies include seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, and engaging in stress-relieving activities. Understanding that scabies is a common and treatable condition can also alleviate anxiety and embarrassment.
Support Systems
Having a strong support system is crucial for individuals dealing with scabies. Friends, family, and healthcare providers can offer emotional support and practical advice throughout the treatment process. Encouraging open communication and understanding can help individuals feel less isolated and more empowered to tackle the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to cure scabies?
The treatment duration for scabies varies depending on the severity of the infestation and the type of treatment used. Typically, symptoms begin to improve within a few days of starting treatment, but it may take up to four weeks for the skin to heal completely and for all symptoms to subside.
Can scabies go away on its own?
Scabies does not resolve without treatment. The mites continue to reproduce and burrow into the skin, worsening symptoms if left untreated. Seeking medical advice and starting a treatment plan is essential for eradicating the infestation and alleviating symptoms.
Is scabies contagious?
Yes, scabies is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infested person. It can also spread through contact with contaminated items such as bedding, clothing, and towels. Preventing the spread requires treating all close contacts and maintaining good hygiene practices.
What are the complications of untreated scabies?
Untreated scabies can lead to secondary bacterial infections due to excessive scratching and skin damage. In severe cases, scabies can cause crusted or Norwegian scabies, characterized by thick crusts on the skin and a higher mite population, requiring more intensive treatment.
How can I prevent scabies reinfestation?
Preventing reinfestation involves treating all household members and close contacts simultaneously, thoroughly cleaning the living environment, and avoiding sharing personal items. Regularly washing bedding and clothing in hot water and maintaining good personal hygiene are also crucial preventive measures.
Are there any side effects to scabies treatments?
Some individuals may experience mild side effects from scabies treatments, such as skin irritation or redness. If side effects persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare provider for alternative treatment options or adjustments to the current regimen is recommended.
External Resources and Links
For more information on scabies, its treatment, and prevention, visit reputable health organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) [CDC Scabies Information](https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/index.html).
Conclusion
Scabies is a common and treatable skin condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate management to prevent complications and spread. By understanding the nature of scabies and exploring both conventional and natural treatment options, individuals can effectively cure scabies and improve their skin health. Maintaining good hygiene, boosting the immune system, and seeking professional medical advice are key components of a successful treatment plan. With the right approach, scabies can be managed and eradicated, allowing individuals to regain comfort and confidence in their skin.
Article Recommendations